Galvanostatic charge–discharge tests, 57Fe and 119Sn Mössbauer and XRD measurements on novel Sn-Ni-Fe electrodeposits
The paper authored by
G.B. Lak,
E. Kuzmann,
M. El-Sharif,
C. U. Chisholm,
S. Stichleutner,
Z. Homonnay and
L. Sziráki
is published in Hyperfine Interactions (2013, vol. 218, pp. 145–150).
Abstract:
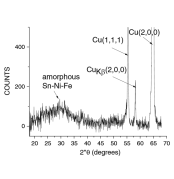
Novel Sn–Ni–Fe ternary alloys were successfully deposited by pulse plating technique from an electrolyte based on sodium gluconate which acts as a complexing agent. XRD results revealed the predominantly amorphous character for the majority of the deposits. 57Fe and 119Sn conversion electron Mössbauer spectroscopy indicated the formation of a paramagnetic amorphous alloy using a short on-pulse duration and where the Fe content was less than 22 wt.%. Galvanostatic charge–discharge tests of the novel Sn-Ni-Fe deposits were carried out in a model Li-ion cell and indicated that the Sn-Ni-Fe alloys have potential as an electrode material.
