Electrochemical nanogravimetric study of the electropolymerization of 6-aminoindole and the redox transformations of the polymer formed in aqueous media
The paper authored by
B.B. Berkes,
Á. Nemes,
C.E. Moore,
F. Szabó and
G. Inzelt
is published in Journal of Solid-State Electrochemistry (2013, vol. 17, pp. 3067–3074).
Abstract:
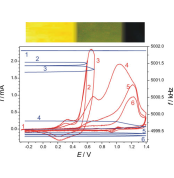
The electrochemical quartz crystal nanobalance was employed to study the electropolymerization of 6-aminoindole on gold electrodes in acidic media. Potentiostatic or potential cycling electrooxidation of 6-aminoindole below 0.5 V vs. saturated calomel electrode leads to the formation of multilayer polymeric films, while at higher positive potentials, further oxidation takes place resulting in a different material which remains attached to the metal surface but shows decreased or no redox activity. A mechanism of the redox transformations of poly(6-aminoindole) which involves protonation–deprotonation accompanying the electron transfer is suggested. In this potential range, a yellow-green reversible color change occurs. At higher positive potentials blue-purple, indigo-type compounds are formed, and bond-breaking leads to the decrease of the electroactivity.
