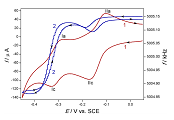
Study of the surface mass changes during the redox transformations of copper(II) phthalocyanine-tetrasulfonic acid on gold in acidic media
The paper authored by
G. Inzelt,
A. Nemes and
A. Sajti
is published in Journal of Solid State Electrochemistry (2017, vol. 21, pp. 1725–1732).
Abstract:
An electrochemical quartz crystal nanobalance (EQCN) has been used to study the deposition (adsorption) and dissolution (desorption) during the redox transformations of the water-soluble copper phthalocyanine-tetrasulfonic acid (CuPcTS) on a gold electrode in contact with aqueous acid solutions. The anomalous cyclic voltammetric responses that had been observed invoked the application of the EQCN technique. Indeed, it became evident that during the electroreduction in certain potential ranges, deposition/dissolution processes take place on the gold surface. Surprisingly, complex changes have been observed even when the cyclic voltammetric curves seem to be regular, i.e., characteristic to the responses of soluble redox pairs. Beside the cyclic voltammetry, EQCN was combined with galvanostatic measurements detecting the chronopotentiometric curves with the simultaneous mass changes. A reaction sequence has been suggested for the elucidation of the events occurring during the reduction and reoxidation of CuPcTS.
