Studying the effects of bismuth on the electrochemical properties of lead dioxide layers by using the in situ EQCM technique
The paper authored by
Balázs Broda and
György Inzelt
is published in Journal of Solid State Electrochemistry (2020, vol. 24, pp. 2733–2739).
Abstract:
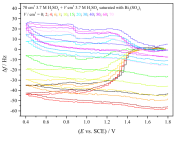
The charge-discharge characteristics and the aging mechanism of PbO2 layers doped with bismuth in contact with sulfuric acid solutions were studied by using combined cyclic voltammetry and electrochemical quartz crystal microbalance (EQCM) techniques. For this purpose, thick lead dioxide layers (non-doped and doped with Bi) were electrodeposited on gold substrate from aqueous solutions of Pb(NO3)2 dissolved in nitric acid and they were investigated in sulfuric acid media. Based on the electrochemical and the mass change responses, it is concluded that during the electrodeposition, bismuth influences the structure of the PbO2 formed. Bi(III) also inhibits the oxidation of lead sulfate and affects the reduction kinetics of lead dioxide. During successive cyclization (aging), the presence of bismuth accelerates the hydration of PbO2.
